Here explains the switching frequency at PFM control and the switching current between PWM mode and PFM mode.
The switching frequency of DC/DC converter is especially important for the application of noise-sensitive RF / audio, etc.
As the noise generated from DC/DC converter (conduction / radiation noise) contains nth harmonics of switching frequency, it is necessary to select DC/DC converter so that the switching frequency does not affect the system. If you can forecast the switching frequency without implementing operation of actual machine, you can select a DC/DC converter optimum for the system before confirmation of actual machine and it considerably contributes to man-hour reduction.
1. Execution of simulation (select the IC / input the power supply specifications)
Input the simulation conditions for the input items and execute the simulation.
Step 1. Select a product
Step 2. Select oscillation frequency
Step 3. Select an operation mode
Step 4. Input the power supply specifications (Vin / Vout / Iout / peripheral component values etc.)
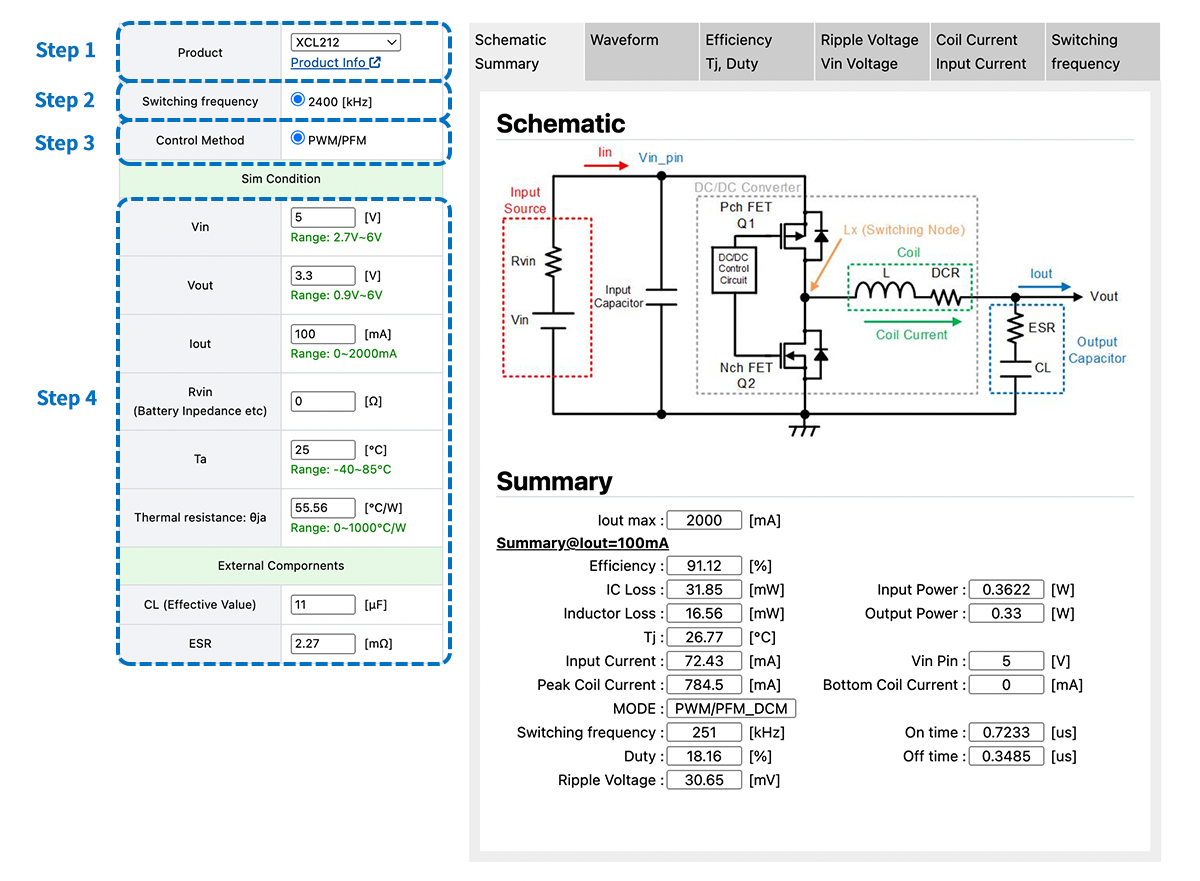
2. How to confirm the switching frequency mode at PFM control
It is possible to confirm the switching frequency from "Summary" tab or "Switching frequency" tab. For the output current dependency of switching frequency, confirm "Switching frequency" tab.
Here, let's confirm the switching frequency of PWM/PFM control type step-up DC/DC converter XC9142 series 1.2 MHz as a concrete example.
Under the condition Vin = 3.3V / Vout = 5V, the switching frequency when Iout = 1μA is about 580Hz. You can see that the switching frequency increases while the output current increases.
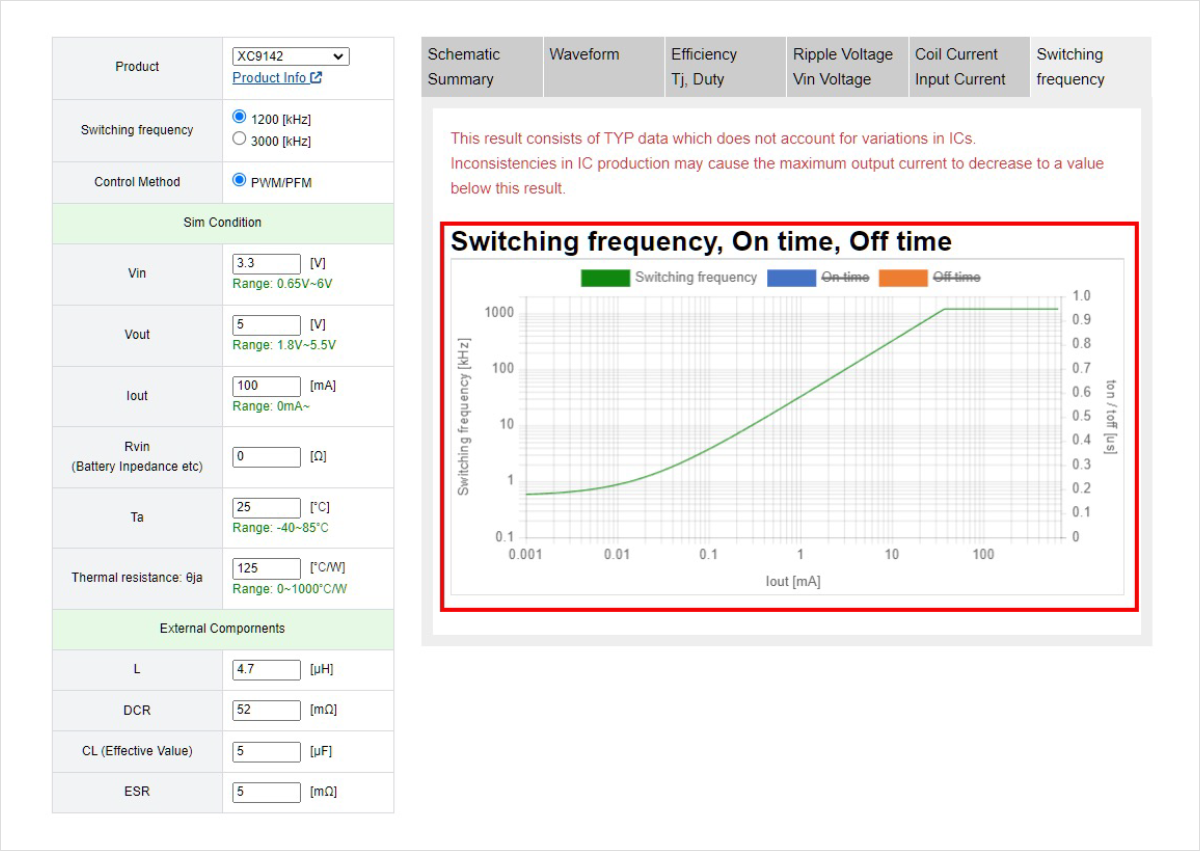
3. Switching current in between PWM control and PFM control
Next, confirm the switching current in between PWM control and PFM control.
Let's confirm the switching current in between PWM control and PFM control referencing PWM/PFM control type step-up DC/DC converter XC9142 series 1.2MHz in the same way as previous section.
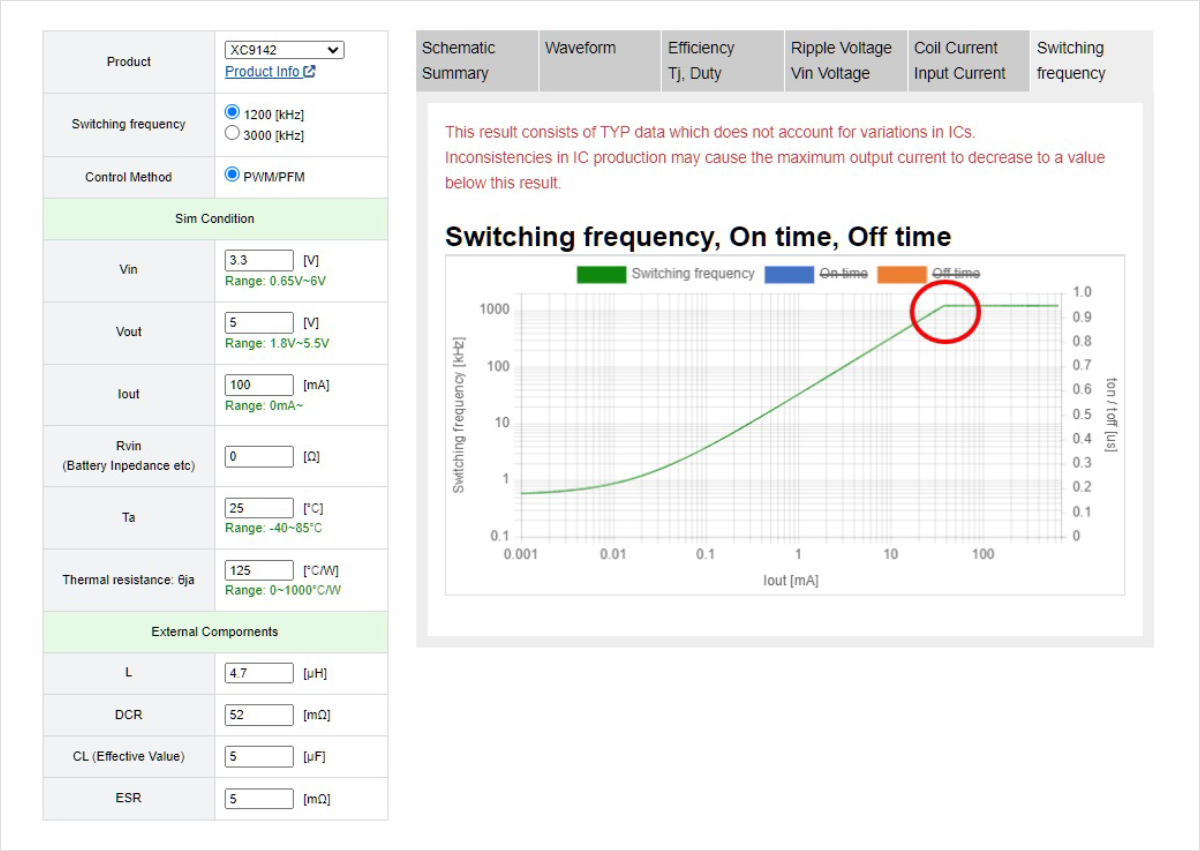
The output current increases. The point when the switching frequency reaches the oscillation frequency of PWM control is the switching current in between PWM control and PFM control.
Under the conditions Vin = 3.3V / Vout = 5V, you can see that the switching between PWM control and PFM control occurs when Iout = about 40mA.
CAUTION: Notes on power supply specification dependency / misalignment from actual machine of switching frequency for PFM control
The switching frequency of simulation is sometimes out of that of actual machine due to the following factors. Utilize the switching frequency of simulation as a rough indication.
1. Fluctuation due to input voltage / output voltage / inductance value
Even for the same IC, the switching frequency varies due to input voltage, output voltage, or inductance value.
In addition, the switching frequency fluctuation tendency due to input voltage, output voltage, or inductance varies depending on the control method of IC.
For this reason, sufficiently confirm the tendency of switching frequency under the conditions to be studied.
2. Misalignment between simulation result and actual machine
This simulation is executed assuming ideal PFM operation.
However, with the actual product, continuous switching at PFM control may make superimposition or switching of ripple voltage frequency lower than the simulation result.
Moreover, the switching of PFM control between PWM control may not be smoothly implemented.