PSRR is the abbreviation for Power Supply Rejection Ratio and is an indicator for how small the input voltage change can be made in relation to the output voltage change.
It is often used as an indicator to express the transient response characteristic of voltage regulators.
The transient response characteristic is a characteristic for which it is difficult to compare the transient response capability between products when the conditions of the measured output currents are different.
However, with PSRR it is easier to match the measurement conditions than it is for the transient response characteristic. In addition, since the transient response characteristic also tends to be faster for voltage regulators with a good PSRR, PSRR is used as an indicator for quick response.
The above simple explanation makes it difficult to just what PSRR is, so let’s use a concrete example to explain PSRR.
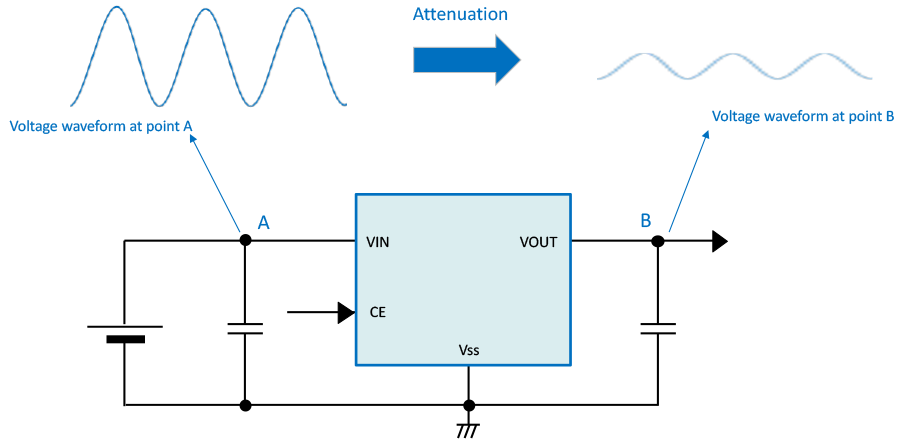
Power Supply Rejection Rate (PSRR)
This shows the ratio of output voltage change ΔVOUT when a voltage ΔVIN with a frequency component is input to the input terminal.
PSRR(dB) = 20log(ΔVOUT/ΔVIN)
⇒20dB : ttenuates to 1/10
40dB : Attenuates to 1/100
80dB : Attenuates to 1/1000
The PSRR is a characteristic that shows how small the sine wave applied to the voltage regulator input side can be made at the output side. In the above diagram, this shows how stable the output voltage at Point B on the output side can be made when a sine wave is applied to Point A on the input side.
For example, when a 1kHz 500mVp-p sine wave is applied to the input side, to hold the output side change to 5mVp-p, the attenuation is to 1/100 (5mVp-p/500mVp-p), so the PSRR is 40dB@1kHz.
The PSRR depends on the frequency, and the value at 1kHz is generally used in specification notes, so be careful of the frequency when the specified frequency is different.
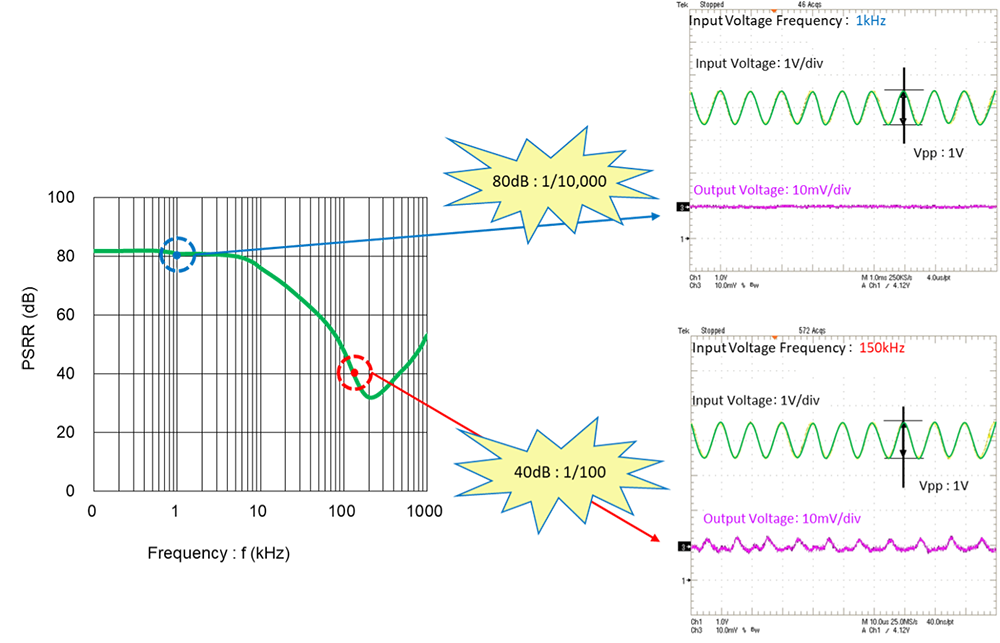
This shows the PSRR for an actual product.
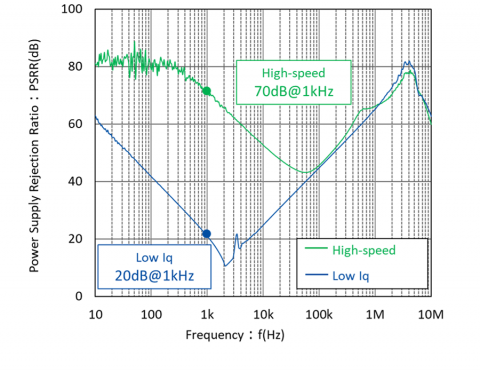
The high-speed type is 70dB (=1/3200) at 1kHz, but the low consumption type is 20dB (=1/10), so we can see there is a large difference in the PSRR. Generally, the high-speed type PSRR tends to have a higher PSRR on the low-frequency side.
When the sway component from the input side changes from low frequency to high frequency, the IC becomes unable to respond and the PSRR gradually declines. In this case, the sway component that could not be removed is transmitted to the output side.
If the frequency becomes even higher, the PSRR changes from a decreasing tendency to an increasing tendency. This makes it completely impossible for the IC to respond to the high frequency and shows that the driver FET’s on resistance is fixed.
In this state, an RC filter is formed by the driver FET fixed on resistance and the output capacity, so the PSRR demonstrates an increasing trend.